Are you aware that 11.1% of emails sent don’t land in the inbox because of email deliverability issues? This can impact your cold email campaign rendering your efforts futile. After all, your aim to reach prospects, not spam filters!
So, what can you do about it? The answer is simple, you have to focus on improving email deliverability, and that is exactly what we will see in this guide.
Let’s start with what email deliverability is, why it is important before we jump to how we can increase it & what best practices to follow for a good sender reputation.
So without much ado, let’s begin.
Table Of Contents
- What Is Email Deliverability?
- What Email Actions ISPs Value?
- Negative Effects Of Poor Email Deliverability
- How To Increase Email Deliverability?
- Determining Sender Reputation
- Best Practices For A Good Sender Reputation
- How ISPs Affect Email Deliverability?
- Email Actions Valued By ISPs
- Deliverability Factors In Your Control
- Email Infrastructure And Authentication
- Important Do’s And Dont’s Of Email Deliverability
- List Of Tools To Improve Deliverability
- FAQs
What Is Email Deliverability?
With marketers and salespeople depending on email, getting emails to the recipient’s inbox is essential. If emails don’t hit the inbox, recipients won’t be able to read them, leaving the effort of the senders futile. So, you have to make sure the email reaches the inbox. And that is called email deliverability.
In other words, cold email deliverability refers to a set of processes that enable placing an email into the inbox of the intended recipient.
Email deliverability is crucial for an email campaign to succeed, and as a salesperson, it requires effort from your end.
What Email Actions ISPs Value?
To improve cold email deliverability, you have to think like those who make it possible to send an email: the ISPs or Internet Service Providers.
You can start by looking at the number of emails sent on a daily basis. It is to the tune of 300 billion. More than half of those are business emails. The number is enormous, but can you believe that around 50% of these emails are spam? This means around 100 billion emails struggle to land in the recipient’s inbox.
To counterattack cold email spam, ISPs ensure that spam emails don’t even hit recipients’ spam folders, leaving alone letting them into the inbox. Thus, ISPs project themselves as saviors of recipients. ISPs are strict and penalize spammers or else it will not be easy to handle such large volumes of emails.
You have to start thinking like an ISP to improve your cold email deliverability. ISPs know who you have emailed previously, and they are also aware of your click-through rate. If no one opens your mail, your emails will eventually start landing in the spam folder or even worse, not get delivered altogether.
The crux of the matter is that you want to get your email delivered to your prospect’s inbox as a salesperson or marketer. That is the real goal of email deliverability.
Negative Effects Of Poor Email Deliverability
What will happen when you have poor email deliverability? Here are some of the cons,
a. As emails don’t hit the inbox, the recipient won’t be able to open or read them
b. The latest news won’t reach new and existing customers.
c. Important messages like shipping details and password reset won’t reach customers.
d. As emails don’t get delivered, it will be a loss for your business due to low ROI.
e. Rivals having better deliverability will appear more in inboxes.
f. Tracking key performance metrics such as open rates and click-throughs won’t be possible.

How To Increase Email Deliverability?
One way of increasing cold email deliverability is by having a good sender reputation.
An ISP gives a score to the IP address and domain you use for sending emails. It is referred to as the sender’s reputation.
You can compare it with your credit score that is painstaking and time-consuming to build but super easy to ruin in a short time! A higher sender reputation will fetch you good deliverability, as already mentioned, and a poor one would either result in rejection of your emails or place them in the spam folder.
According to a study, almost half the cold email deliverability problems are due to poor sender reputation. Talking about numbers, do you know how much your sender reputation should be? Ideally, it has to be above 80, and in case it is not so, you have to work towards improving it.
You must note that fluctuating between an average and a good sender reputation is not a problem. There are times when you have to send emails to an unengaged segment of your mailing list because of your new email campaign. It will make your sender reputation drop a little, but it is okay. You can work towards building it up again.
Determining Sender Reputation
Sender reputation is determined by two factors – IP reputation and domain reputation. Both have a considerable impact on deliverability.
IP reputation
A computer or a server that sends emails has a unique identifying address called the IP address. It is easy for ISPs to track senders using an IP address. The IP reputation depends entirely on the IP address from where the email originated. There is no link with the brand that is sending the email.
Your IP reputation is what makes you get into the server of the recipient.
As an email sender, you can use your dedicated IP address to send emails or make use of a shared IP pool.
Using a dedicated IP address means that you send all emails through one single IP address. As others don’t use that IP address, you are responsible for whatever is sent through it. It thus pushes the deliverability entirely on you and makes it difficult to recover from mistakes. Ideally, dedicated IP addresses seem to be suitable for larger businesses that have a high email volume. They usually have the resources needed to implement best delivery practices.
A shared IP pool has many companies sharing IP addresses to send mails. In this case, email deliverability is not the responsibility of one company but is a shared responsibility. However, this makes the poor practices of others affect your deliverability. But on the brighter side, you can be at an advantage with the increased volume of emails.
It is well-suited for small businesses that don’t have a high email volume required to get a good sender reputation. Also, a shared IP pool protects small senders from getting impacted by mistakes thanks to the high email volume.
Domain reputation
It is your domain reputation that gets you into the inbox of recipients. Domain reputation is connected to the brand that sends the email.
Even if your IP address gets changed or if your ISP changes, your domain reputation will stay with your brand. This can benefit you if you have worked hard in building a good reputation.
Domain reputation partly depends on the kind of industry you are in. Generally, ISPs are stricter with banking and finance companies than they are with retail and travel businesses. Domain reputation has more to do with what type of sender you are, whether you segment your lists, send emails to inactive accounts, and so on.
Email segmentation
Email segmentation is the practice of organizing your mailing lists into smaller groups referred to as segments. It helps you send emails to a specific segment instead of the entire mailing list. In addition, it helps to manage your reputation.
Here’s how you can do your segmentation to get maximum deliverability.
Segment 1- No consent
This is a segment containing email addresses that have not given their consent to receive emails from you.
You mustn’t email this segment.
Note: This is not the case with cold emailing, where you reach out to prospects who don’t know you.
Segment 2- New (less than 30 days old)
This segment has newly-added email addresses that are less than 30 days old.
You can send this segment a good number of emails, including ones to welcome them on board. The mail frequency to this segment can be 1-3 emails a week.
Segment 3- Passive (31 to 90 days old, no open or clicks)
These email addresses are 1-3 months old, and they don’t open or click your emails. With this segment, you still have a chance of them engaging with your emails. However, consider reducing the frequency of your emails so that they don’t move away.
Don’t have more than 2% of passive accounts on your mailing list.
Keep the mailing frequency to 1 email per week.
Segment 4 – Active (more than1 month old, open or click done within 90 days)
These accounts engage with your emails, and that renders them eligible for receiving your highest email frequency. Your mailing list should have a minimum of 40% active accounts. It is impressive if you have 65% or more on your list.
Segment 5- Lapsing (more than one month old, last activity was 91-180 days ago)
These email accounts are the ones that didn’t engage with your emails in the last 90 days but had some activity within the last 180 days. They are withdrawing from you probably because you are sending similar content to them each time.
Try sending fresh content to them along with making use of personalization techniques. Also, reduce the frequency of emails for this segment.
Segment 6- Lapsed (More than one month old, last activity was more than six months ago)
These email accounts are no longer interested in your email. So when ISPs see that users have not engaged with your emails in the last six months, they send your emails to the spam folder.
These accounts can be spam traps about which you will learn later in this guide. Sending emails to spam traps can affect your sender reputation negatively. As these lapsed email addresses bring very little revenue to you, it is better to remove them from your mailing list.
Best Practices For A Good Sender Reputation
Let’s take a look at the best practices you should follow for a good sender reputation,

1. Maintaining low bounce rates
Bounce rate is the percentage of email addresses that the recipient’s mail server returns.
Your bounce rate will be 2 percent if 20 messages bounce out of the 1000 emails you sent.
An email bounce of two types,
Hard Bounce: A hard bounce is an email message that gets returned to the sender as the recipient’s address is invalid. The main reason for this to occur can be a non-existent domain, an inactive email account, or the recipient being unknown.
Soft Bounce: A soft bounce is an email that reaches the recipient’s mail server but gets returned undelivered before reaching the recipient. One main reason for a soft bounce to occur is the recipient’s mailbox being full temporarily.
The key to improving your sender reputation involves keeping the bounce rate as low as you can. A high bounce rate may make ISPs think that your emails are spam.
To maintain low bounce rates, you should clean your email lists regularly. You must also get rid of hard bounces, complaints, and contacts with whom you have not engaged in a long time.
Send emails to those who have opted-in.
2. Keeping the complaint rate low
When a recipient marks an email as spam, it is a complaint. They are red flags to ISPs and indicate that recipients are not happy with your email. With an increase in the complaint rate, there will be a drop in sender reputation, making it difficult to reach out to recipients in the future.
Ideally, you must try to keep it below 0.1% of the emails you send. Doing so is essential because ISPs are very serious about spam complaints and have a very low tolerance for them. Ensure that you remove the email addresses from your list that have made a complaint so that you don’t send an email to them again.
3. Do proper formatting of emails
While bounce rates and complaints are always under the scanner of ISPs, the formatting of your email content also impacts how ISPs handle your emails. You have to make sure that you send quality emails because inboxes are already quite cluttered, making it even more essential to send emails with quality content. Here is what all you should have your focus on,
1. Proper HTML formatting – ISPs often spam emails with poor coding. Therefore, you must focus on ensuring the proper HTML formatting.
2. Visibility of the unsubscribe link – Recipients should have access to an easy way to opt-out of your emails that is an alternative to marking the email as spam.
3. Compatibility of your email across most email clients – You have to ensure that your email is compatible with different email clients. It will make your email look relevant irrespective of the email client used by the recipient.
4. Being mobile-friendly – Many people check their emails on mobile devices, making it evident that you have to keep your email content mobile-friendly. The recipient should not have a problem while viewing the email on a tab or smartphone.
4. Avoiding spam traps
To maintain a good sender reputation, you have to avoid spam traps as much as you can.
A spam trap is an email address that doesn’t belong to a real person. Owned by an ISP, it can be an abandoned email address that the ISP reclaimed (referred to as recycled spam trap) or a new email address created to function as a spam trap (referred to as pristine spam trap).
Whatever it may be, recycled or pristine, a spam trap should not be a part of your mailing list. Sending emails to spam traps can ruin your sender reputation, and you must avoid them as far as possible.
Following is how to do it,
1. Create a segment of unengaged email accounts.
2. Stay away from purchased email lists.
3. Scan your mailing list for email addresses with typos.
4. Keep a close eye on bounces that can turn into spam traps.
5. Trying hard to stay off the blacklist
When an ISP blacklists you, you can’t send emails. It isn’t easy to get off the list, so it is better to avoid getting into it. You will learn more about blacklists in the following section.
So, we have seen what the best practices are to improve sender reputation.
Let’s know a bit about the negative role of ISPs in cold email deliverability.
How ISPs Affect Email Deliverability?
To keep spammers away, ISPs try a lot of different things. However, owing to the large volume of emails they manage, their attempts can negatively affect your cold email deliverability. Here’s what ISPs use to curb the activities of spammers.
1. Sending limits
ISPs set a sending limit for every sender. It refers to the number of emails they think are acceptable and normal for sending in a specific period. As soon as you touch the sending limit, ISPs soft bounce the emails you send post reaching the limit. You have to wait for the limit to reset.
The sending limit is different for everyone. There is a weekly limit for some senders, while for others, there is a daily limit. It all depends on the volume of emails you are sending. Moreover, the strictness of the sending limit is based on your sender reputation. However, regardless of how good it is, the emails will get soft bounced when you send way too many. But, you can avoid soft bounces by slowly increasing your email volume.
2. Blocks

When the ISP blocks you, you won’t be able to send emails. It happens when they receive too many spam complaints or when too many emails get hard bounced.
The block can be indefinite, but most often, it lasts for two days to one week. Some ISPs require you to contact them when you get blocked and show them that you have made alterations in your sending practices.
It is way better to avoid ISP blocks than to look for ways to get yourself unblocked. To prevent getting blocked,
a. Have a clean mailing list so that there are no hard bounces.
b. Segment your mailing list to mail only engaged recipients.
c. Make unsubscribing easy for the recipient so that spam complaints are minimal.
3. Email bulking
When ISPs send your emails to junk or spam by default, it is referred to as bulking. The recipients won’t view your mails this way as most people don’t check their spam folders regularly.
4. Blacklisting

A blacklist is a list of sender domains and IP addresses that the ISPs have caught sending spam.
When a blacklisted sender sends an email, the chances are that it will end up in the junk folder or not reach the destination at all.
It is a severe form of a block, and to get removed from it, you have to appeal to the blacklisting organization. Therefore, it is better to not land on a blacklist in the first place.
So, how can you find out whether the ISP blacklisted you?
Some tools help you perform a check about your blacklist status.
Whatever it may be, you have to try your best to not appear on a blacklist, or your sender’s reputation would get tarnished.
Email Actions Valued By ISPs
ISPs value certain actions of recipients, and they have both negative and positive reactions. Let’s take a look at them,
Positive reactions
a. Message read – ISPs track which messages were read and which weren’t. In addition to that, the longer the message stays on the screen adds more value to this metric.
b. Moved to folders – When users place emails in folders, it means that they want to keep the message safe and wish to receive more from the sender.
c. Message forwarded – When an email message is forwarded, it indicates that the user expected it and desired it.
d. Sender’s email address added to address book – When the sender’s email address is in the recipient’s address book, it guarantees that emails will enter the inbox no matter how poor the metrics are.
e. Message marked as not spam – ISPs find an email marked as not spam by the recipient to be a crucial metric. It shows the sender in good light as marking a message as not spam requires the recipient to put in the effort.
Negative reactions
a. Messages deleted after the recipient read them – Reading a message may seem to be a positive reaction. Still, when the recipient deletes the message after reading it, it indicates that the message was of no use to the user.
b. Messages deleted by the recipient without reading them – This is an adverse reaction, and it makes the ISP understand that the message was not of interest to the user. Sending emails repeatedly to an account that doesn’t engage with the emails can result in future emails getting filtered out.
c. List Unsubscribes – ISPs track clicks recipients make to unsubscribe from the sender’s mailing list. It is evident that when a recipient chooses to unsubscribe from a list, the person no longer wants to receive emails from the sender.
d. Blocking sender’s email address – Some ISPs allow recipients to block a sender’s address so that they don’t get messages from that sender in future. This is by far one of the most negative reactions.
e. Message marked as spam – This strongly indicates that the recipient does not want to receive your email. All emails sent after this action will end up in the spam folder of the recipient. This increases the chance of getting filtered out in the mailbox of other recipients too.
Deliverability Factors In Your Control
Certain factors have a huge impact on deliverability, and they are,
1. The quality of your mailing list
Having a clean mailing list has a tremendous impact on deliverability. You must try your best to maintain the quality of the emails on your mailing list. It is of more importance to a new sender or a new IP address as the ISP knows nothing beyond it about you.
2. Email frequency and relevancy
ISP will be stricter with you if you send emails daily. Also, there is no specific sending frequency because it depends on your industry. For example, a hiring company might send emails in bulk every day, whereas a wedding planning company occasionally sends emails.
As discussed, you must try to segment your mailing list so that you don’t send the same message to everybody on your list. This will ensure that you are sending emails that are relevant to recipients. Along with relevancy, personalizing email content also has a significant impact on engagement and deliverability.
3. Email content and format
Maintaining the quality of your content and formatting them in a non-spammy way matters. However, at times, spam-like emails from those with a high sender reputation have fewer issues with deliverability than valuable emails from someone with a poor reputation. Whatever it may be, you must try to make the content look non-spammy from your end as it is a deliverability factor in your control.
4. Sender reputation
This factor is not much in your control compared to the above factors, but it is of high importance and requires your attention.
Email Infrastructure And Authentication
Email deliverability has infrastructure and authentication at its core. If they are not set up correctly, there is a considerable chance of facing issues with email delivery.
Email infrastructure refers to background processes that enable getting your email delivered. Email authentication is a way of providing proof to ISPs that the email is from you and not from a forge.
Firstly, let’s take a look at email infrastructure,
Email Infrastructure
Successful cold email deliverability is possible only when you have a strong email infrastructure. It is a bedrock that includes IP addresses, your Mail Transfer Agent, Bounce Handling, and many more.
The following are the eight major things to consider about your email infrastructure,
1. Make use of the latest encryption standards
TLS Encryption – Transport Layer Security or TLS is a protocol that helps you keep messages confidential by encrypting them when they are en route. It protects the privacy of both the sender and receiver and prevents the manipulation of the message by fraudsters.
MTA-STS – This is a new encryption standard that insulates email transmissions and prevents attacks. That ensures security and privacy.
2.Use a dedicated IP address when sending high volumes of emails
We have seen earlier that you can try to imrpove your sender reputation by using a dedicated IP address because you are the only one sending emails over the IP address. That means there is no fear of getting affected by other senders. However, it is suitable only for those organizations that send high volumes of emails (more than 100k emails annually).
3. Use a shared IP address when sending less than 100k emails a year
When you use a shared IP address, other senders are also using the same address. The benefit is that the best practices used by other senders will boost your sender’s reputation as well. Using a shared IP address is the best bet for smaller organizations that send below 100k emails a year.
4. Use feedback loops to manage spam complaints
Knowing when there is a complaint about your email can help tremendously. But how do you find it out? Simple. Use a feedback loop.
A feedback loop reports complaints, such as the recipient clicking on the spam or junk button. When you know which email account has made the complaint, you should remove them from the mailing list. That way, you won’t send emails to them anymore.
5. Make sure that you can receive emails on your ‘from address’
Making sure that your ‘from address’ can receive emails is essential. It will let your recipient reply to your email that enables better engagement. Upon replying to your email, your address gets into the contact list of recipients that makes sure that next time your email will land in the inbox.
6. Setup engagement tracking
Get the details of how recipients interact with your content, such as opening your email and clicking links. You can then work on improving deliverability. For example, you can delete the email addresses of recipients who mark your email as spam.
7. Manage bounces
As already discussed, it is crucial to keep your bounce rate as low as you can for your sender reputation and email deliverability.
Processing systems like a Suppression List will help you figure out the reason behind email bounces and how to fix them.
8. Use real-time monitoring to detect and fix issues
Having a real-time monitoring service in your infrastructure is essential to find out deliverability issues and tell you where the problem lies.
Email Authentication
Email authentication is proof to ISPs that the email sent from you is actually from you and is not forged by another person. ISPs want authentication as it helps them curb malicious activities like phishing and spamming.
Why is there a need to authenticate your email?
There is a need to authenticate your email to stand out in the crowd of spammers and bad senders in the inbox. There are three standards used for email authentication, and they are DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail), SPF (Sender Policy Framework), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, & Conformance).
Here’s what these mean,
DKIM makes sure that the message that came into your inbox did not get maliciously altered during transit.
SPF is an email authentication protocol that lets you mention which IP addresses have the authority to send an email on behalf of your domain.
DMARC brings SPF and DKIM authentication together into a common framework by ensuring that legitimate email is authenticated against the two standards SPF and DKIM.
Important Do’s And Dont’s Of Email Deliverability
Here’s a list of the critical do’s and don’ts of cold email deliverability. They will give an idea of whether you are following the best email practices or not. They will help you know how to send cold emails without getting blocked.

Email Deliverability – What to avoid
1. Purchasing or renting email addresses
The quality of your mailing list is of paramount importance when you talk of cold email deliverability. Purchasing addresses in bulk is not a good practice because you might not know how many email addresses from the list are valid. Additionally, buying mailing lists is against the guidelines of regulations like GDPR.
2. Sending unsolicited emails
Avoid sending emails to those who don’t want to receive them. Or else the sender will mark them as spam, which can negatively impact your sender reputation. In addition to that, It is also a violation of GDPR and can draw a penalty.
3. Sending emails to group email addresses
ISPs are not okay with you sending emails to group email accounts like info@.xyz.com or @sales@abc.com. They disapprove of this activity as they want you to send emails to individuals. Additionally, there is also a high probability of someone in the email group marking your email as spam. It can affect your sender reputation.
4. Sending emails to inactive accounts
These are email accounts that have not engaged with your emails in the last 6 months. These don’t bring you any revenue and harm your metrics. You can remove them from your mailing list or transfer them to the re-engagement program.
5. Using Spammy language in emails
Avoid sending emails with spammy language. Using all caps, excessive punctuation, terms like ‘sales’, ‘super hot’, ‘exclusive’ can annoy both your recipients and ISPs. If you want to avoid getting penalized, you have to make sure your email doesn’t look spam. ISPs have no tolerance for spam.
Email Deliverability – What to do
1. Sign up to services such as Google Postmaster, Yahoo feedback, and Microsoft SDNS to know about your reputation on the respective ISPs. This way, you would know what improvements you have to make.
2. Keep the sign-up process a memorable one so that people remember you and are less likely to mark emails from you as spam. Use a double opt-in sign-up which makes the user click on the confirmation link sent to their email. Also, the success rate is 70 percent with this method of signing up. Alternatively, you can use CAPTCHA to steer clear of spambots.
3. Match email frequency to email engagement. Make use of segmentation for this. The segment of your mailing list that is most engaged should get the maximum emails.
4. Use spam checking tools to score your email content. It would prevent your emails from getting blocked.
5. Review the reports of your campaign. Monitor bounce and complaint rates at the level of an ISP. Look for signs that your emails are going to spam folders.
6. Check how emails appear for everyone. Some tools help you know how your email looks on different devices and browsers. When recipients can’t see email properly, they won’t engage with them and mark them spam. On the other hand, perfectly rendered emails increase your value in the minds of ISPs.
7. Limit your image size to 100KB and maintain a suitable text-to-image ratio. The reason is that ISPs like emails to have more text than images. So, better keep it to 60:40.
8. Unsubscribing from your emails should be simple. If you don’t do so, you can expect spam complaints. Many regulations require making unsubscription easy for the recipient.
9. Make use of personalization. With personalization, engagement increases, and that is good for both your sender reputation and your business. Presenting tailored messages byasw2 using various personalization tactics can get you desired outcomes.
List Of Tools To Improve Deliverability
Some email deliverability tools can help you keep your deliverability intact.
1. SalesBlink
With SalesBlink, you can warm up your email domain automatically. Email warmup, when done properly, will improve your sender reputation, and your ESP will know that you are a genuine sender. In addition, this will improve email deliverability, and you will land in the inbox every time you send an email. Therefore, SalesBlink is the tool for you to warm up your email effortlessly.
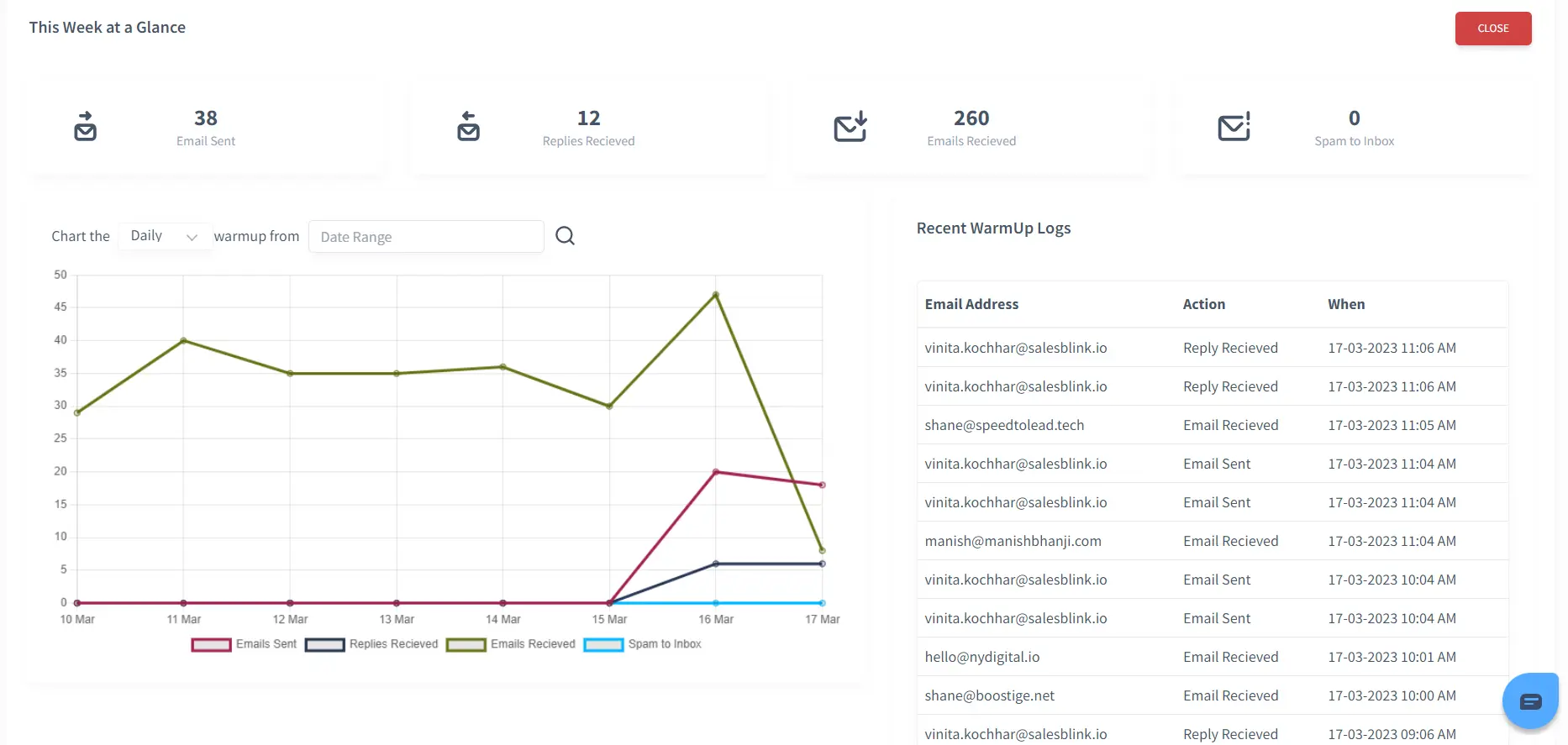
2. MX Toolbox
MX Toolbox Delivery Center helps you understand many things about the email sent from your domain. Right from answering what the sender reputation of the domain is to telling you what you have to do to maintain and improve your cold email deliverability.
3. Mail tester
The tool provides a checklist of what you have to do to fix your domain’s deliverability. And it looks quite handy.
4. GlockApps
Using this app, you can determine why you are not landing in the prospect’s inbox and what you can do. It helps you check email deliverability.
5. Postmaster
This email deliverability software helps track domain reputation every month so that you know where you stand.
Email Deliverability and SalesBlink
SalesBlink is an automated sales outreach tool that ensures that your email deliverability remains high as well. Because if you don’t land in the prospect’s inbox, your email campaign won’t be of any use. Here is what we focus on,
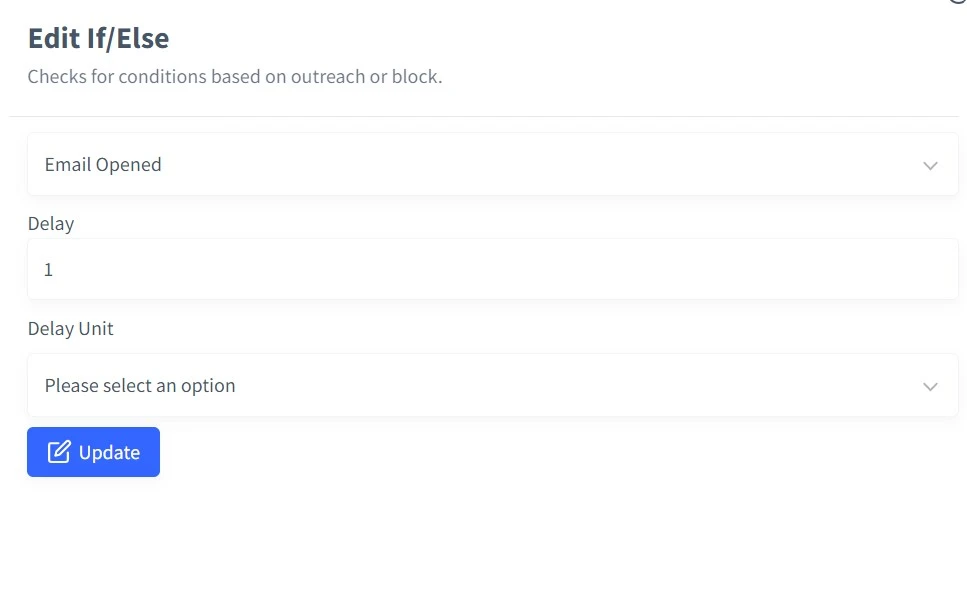
1. Adding delays between emails
If you send consecutive emails with less gap between them, your email deliverability will suffer, and to counter that, we let you add random delays between your emails. The setting won’t affect the emails you scheduled previously.
Here’s how you can add a delay between emails while creating sequences.
2. Setting up a custom domain
Tracking clicks, opens, and replies are crucial to find out how your campaign is performing. For this purpose, you can set up a custom domain, and the receiver’s email server won’t be able to backtrack that the email came through SalesBlink. It provides better email deliverability.
Start Improving Your Deliverability & Sender Reputation To Always Land In The Inbox
Cold email deliverability determines the success of your email campaign, and by no means can you afford to let it down. A poor sender reputation and deliverability will sabotage your campaign, which is why you have to take all the possible measures to maintain a good reputation.
In conclusion, you can increase your chances of hitting recipients’ inboxes and get more engagement by carefully following the best email practices discussed in this guide. More on writing emails in this cold email guide.
FAQs
If emails don’t hit the inbox, recipients won’t be able to read them, leaving the effort of the senders futile. So, you have to make sure the email reaches the inbox. And that is called email deliverability.
Email authentication is proof to ISPs that the email sent from you is actually from you and is not forged by another person. ISPs want authentication as it helps them curb malicious activities
Successful cold email deliverability is possible only when you have a strong email infrastructure. It is a bedrock that includes IP addresses, your Mail Transfer Agent, Bounce Handling, and many more.

Leave a Reply